Part 1: Add a vmdk
1. Shutdown your CentOS 7 VMware and re-launch VMware player
2. Select your CentOS 7 VMware and click "Edit Virtual Machine Settings"
3. In the Hardware tab, click "Add.." button. "Add Hardware Wizard" dialog box will open
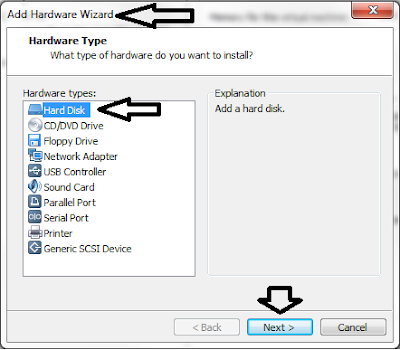
4. In the "Add hardware Wizard", select "Hard Disk". click "Next >"
5. Select "SCSI" as disk type. click "Next >"
6. Select "Create a new virtual disk". click "Next >"
7. Specify disk size in GB and select "Split virtual disk into multiple files." click "Next >"
8. Specify file name of the disk file. recommended to leave it as default. click "Finish".
9. In the "Virtual Machine Settings", you will now see "New Hard Disk" in the "Hardware" tab
Part 2: Configure LVM
1. Scan the host
find /sys -type f -iname "scan" -print
2. You will see the following list as shown below
[root@centos7vm localuser]# find /sys -type f -iname "scan" -print
/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:07.1/ata1/host1/scsi_host/host1/scan
/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:07.1/ata2/host2/scsi_host/host2/scan
/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:10.0/host0/scsi_host/host0/scan
3. Rescan the SCSI bus by passing to each host the "- - -".
# echo "- - -" > /sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:07.1/ata1/host0/scsi_host/host0/scan
# echo "- - -" > /sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:07.1/ata2/host1/scsi_host/host1/scan
# echo "- - -" > /sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:10.0/host2/scsi_host/host2/scan
4. create new pv for the new disk
pvcreate /dev/sdb
5. Now check if the new disk is now available
ls -ltr /dev/disk/by-id/
6. You will see the following list from above command
[root@centos7vm localuser]# ls -lrt /dev/disk/by-id
total 0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Jul 4 15:36 lvm-pv-uuid-eN9yt9-jzpC-7Md5-9N1a-4bdP-i9Dn-jFZ1N4 -> ../../sdb
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Jul 5 2018 ata-VMware_Virtual_IDE_CDROM_Drive_10000000000000000001 -> ../../sr0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jul 5 2018 lvm-pv-uuid-GEwd0z-EDrV-hdB6-0o8M-S8eL-RzqU-gnSCIh -> ../../sda2
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jul 5 2018 dm-uuid-LVM-VhqLdEZRC9TbJfAu3v0q3aUREkRKgZbQl7dtNtoPOoI8yhrsKP3RFs70WdmfTP4o -> ../../dm-0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jul 5 2018 dm-name-centos_centos7vm-root -> ../../dm-0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jul 5 2018 dm-uuid-LVM-VhqLdEZRC9TbJfAu3v0q3aUREkRKgZbQL9essrhuujmOBF6M9VcK2LK0BUEeWlMR -> ../../dm-1
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jul 5 2018 dm-name-centos_centos7vm-swap -> ../../dm-1
7. One of the disk listed above points to our new disk /dev/sdb. in our above list, it's
lvm-pv-uuid-eN9yt9-jzpC-7Md5-9N1a-4bdP-i9Dn-jFZ1N4 -> ../../sdb
8. Get your volume group of the root partition that we wish to expand
vgdisplay | grep 'VG Name'
the output will be as shown below where "centos_centos7vm" is the volume group
[root@centos7vm localuser]# vgdisplay | grep 'VG Name'
VG Name centos_centos7vm
9. Let's now extend the root partition with the new disk
vgextend centos_centos7vm /dev/disk/by-id/lvm-pv-uuid-eN9yt9-jzpC-7Md5-9N1a-4bdP-i9Dn-jFZ1N4 -> ../../sdb
10. Do this command to finalize extending the root partition with the new disk. Note that the command says +20GiB but you can set the value to the size you set your new disk.
lvextend -r -L +20GiB /dev/centos_centos7vm/root
11. Finally, verify the change
[root@centos7vm localuser]# df -k
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/centos_centos7vm-root 41141472 18793492 20444880 48% /
devtmpfs 2006452 0 2006452 0% /dev
tmpfs 2021876 156 2021720 1% /dev/shm
tmpfs 2021876 9180 2012696 1% /run
tmpfs 2021876 0 2021876 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda1 999320 121212 809296 14% /boot
tmpfs 404376 0 404376 0% /run/user/0
tmpfs 404376 12 404364 1% /run/user/1001